Did you know that as many as one in ten older adults in the United States may experience a urinary tract infection (UTI) each year? UTIs in elderly individuals are not just common—they can be more challenging to spot and treat. In this comprehensive guide, you'll discover the key risk factors , expert-backed relief strategies , and practical prevention tips every family and caregiver should know. If you want to protect yourself or a loved one from the higher risk of urinary tract infections in older adults , read on for vital information and quick action steps.
A Surprising Look at Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly: More Common than You Think
When you think of a common health condition among seniors, urinary tract infections in elderly people might not be the first to spring to mind. However, UTIs are among the most frequent infections in older adults, often leading to hospitalizations, especially for those in nursing homes. Unlike in younger populations, symptoms can be vague or atypical—which underscores the importance of recognition and timely care.
Recent studies show that older adults—particularly those with weakened immune systems or chronic health conditions—face a higher risk of urinary tract infection. The infection risk increases with age due to physiological changes, increased medical interventions, and other age-related vulnerabilities. As people age, the body’s natural barriers to infection weaken, making vigilance and prompt action essential to preventing complications.

Why Do Older Adults Face Higher Rates of Urinary Tract Infection?
Older adults experience higher rates of urinary tract infections due to several factors. Anatomical changes, such as weakened bladder muscles and decreased immune system function, make it easier for bacteria to enter and colonize the urinary tract. Additionally, chronic illnesses, reduced mobility, and use of urinary catheters in hospitalized or nursing home patients further elevate the risk of developing tract infections.
Environmental aspects also play a role. Limited access to proper hygiene facilities, incontinence, and changes in routine health monitoring can allow infections to go unnoticed until they become severe. These realities emphasize why older adult urinary tract health must remain a high priority for both caregivers and the healthcare system.
“As many as one in ten older adults may experience a urinary tract infection each year, making vigilance and prompt action critical.” – Leading Geriatrician
What You Need to Know About Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly
Understand why urinary tract infections are prevalent in older adults
Identify symptoms of UTI and distinguishing them from other health condition concerns
Learn the key risk factors for tract infection in the elderly
Recognize quick and effective relief strategies aimed at older adults
Equip yourself with prevention tips for urinary tract infections
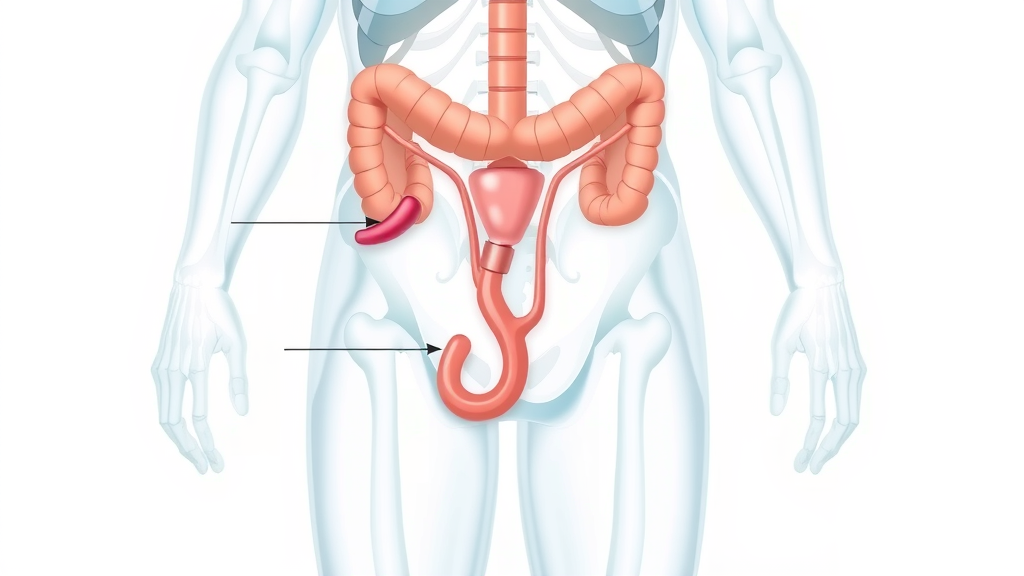
Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly: Defining the Condition and Why It Differs
Urinary tract infections in elderly individuals refer to the invasion and multiplication of bacteria in any part of the urinary tract, which includes the bladder, kidneys, ureters, and urethra. While the basics of this medical condition may sound familiar, UTIs in older adults often differ from those in younger populations. The presentation tends to be subtler or confusing, with symptoms frequently missed or mistaken for other health conditions. This can lead to delayed or inappropriate treatment.
Moreover, older adults are not only more prone to recurrent UTI episodes, but their bodies also respond differently due to slower metabolism and the presence of other medical issues. These factors mean that early identification and tailored management are essential for recovery and long-term urinary tract health.
Urinary Tract Infection vs. Tract Infection: Understanding the Medical Terms
In clinical settings, you’ll often hear both “urinary tract infection” and “tract infection.” The former specifically describes infections impacting any part of the urinary tract (such as the bladder or kidneys), while “tract infection” could refer to infections in either the digestive, respiratory, or urinary tracts.
Because these medical terms frequently get mixed up, healthcare professionals stress the importance of clarifying the affected system. For UTIs, distinguishing the location within the urinary tract (bladder vs. kidney, for example) can guide the most effective treatment strategy for older adults.

Older Adult Susceptibility: Age-Related Vulnerabilities to Urinary Tract Infections
With advancing age, the body’s natural defense mechanisms weaken. The immune system, which is responsible for fighting infections, loses some of its effectiveness in older adults, making it more difficult to fend off bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections. Postmenopausal women are particularly susceptible due to changes in the vaginal flora and reduced estrogen levels, which lower the body's ability to resist infection.
For men, prostate enlargement is a common concern among older adults, potentially causing urinary retention and creating an environment where bacteria can thrive. Combined with possible reduced mobility, hydration challenges, and other chronic diseases, these age-related factors create a perfect storm for recurrent UTI risk.
Common Health Conditions in Older Adults That Contribute to Urinary Tract Infections
Several chronic health conditions place older adults at a higher risk for urinary tract infections. Diabetes, dementia, and incontinence are examples of health conditions that complicate urinary tract cleanliness or elevate the risk of recurrent infections. Diabetes, for example, affects immune system functioning, while cognitive impairments can lead to hygiene lapses or difficulty communicating classic symptoms of a UTI.
Additionally, immobility or neurological diseases can prevent an older adult from fully emptying the bladder, increasing the chance that bacteria linger and multiply. These medical realities mean regular screening and proactive management should be a routine part of elder healthcare.
Key Risk Factors and Causes of Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly
Understanding the critical risk factors for developing urinary tract infections in older adults is the first step toward effective prevention and timely intervention. As people age, their likelihood of experiencing tract infections rises due to both internal and external factors. Family members, caregivers, and older adults themselves should remain informed and vigilant about these risks.
The complex interplay between aging, chronic health conditions, medical device use, and living environments like nursing homes or long-term care facilities contributes to the increased incidence of UTIs in this population.
Risk Factors That Elevate UTI Risk in Older Adults
Major risk factors include advancing age, being female, recent urinary tract procedures, and presence of chronic diseases such as diabetes or kidney stones. The presence of indwelling catheters, a weakened immune system, and poor toileting habits dramatically heighten the risk of infection. Nursing home residents, in particular, experience much higher UTI rates due to their living environment and greater exposure to resistant bacteria.
Dehydration, poor hygiene, and neurological disorders further increase the vulnerability of older people to recurrent UTI episodes. Recognizing these risk factors and implementing targeted strategies is key—especially for those wishing to reduce avoidable hospitalizations and antibiotic use.
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Elderly: When Bacteria Don’t Show Symptoms
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is a unique feature in elderly populations: it’s when bacteria are present in the urine, but the individual displays no classic symptoms of a UTI. This scenario is common in both nursing home residents and community-dwelling older adults. While it might seem alarming, current medical guidelines usually recommend not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria with antibiotics unless specific risks or symptoms are present.
Differentiating between true urinary tract infection and harmless bacteriuria is important because unnecessary antibiotic use can drive antibiotic resistance—something especially concerning in the elderly, who may already be exposed to frequent treatments.

Medical Procedures, Catheters, and Other Urinary Tract Infection Triggers
Medical devices such as catheters are critical tools in healthcare for many older adults, but they bring with them a heightened risk of tract infections. Indwelling urinary catheters provide bacteria a direct route to the bladder, bypassing the body's usual defenses. Additionally, procedures like bladder scans or surgeries can disrupt the urinary tract’s natural barriers.
Even minimally invasive procedures can introduce bacteria, especially if strict hygiene protocols are not followed. As a result, prevention and early recognition of symptoms after medical interventions are critical, particularly for seniors with additional risk factors.
Comparison of UTI Risk Factors in Older Adults vs. General Population
Risk Factor |
Older Adults |
General Population |
|---|---|---|
Catheter Use |
Very Common |
Rare |
Weakened Immune System |
Frequent |
Less Frequent |
Chronic Diseases (Diabetes, Incontinence) |
Common |
Occasional |
Limited Mobility |
Often |
Rarely |
Symptoms of UTI in Elderly: Warning Signs Older Adults Should Never Ignore
Recognizing symptoms of a UTI in elderly patients can be more challenging than in younger groups. While classic symptoms include pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, and cloudy urine, older adults may instead present with subtle or non-specific signs like confusion, fatigue, and sudden incontinence. These warning signs are sometimes mistaken for other health conditions, so prompt evaluation is crucial.
Older adults and their families should stay alert for any changes in behavior, cognition, or urinary patterns. If these changes appear suddenly—particularly if they coincide with fever or changes in urine appearance—seek medical advice as soon as possible.
Classic UTI Symptoms and How They Present Differently in Older Adults
The classic symptoms of UTIs —burning with urination, urgency, and frequent urination—are less likely to dominate in elderly patients. Instead, they may manifest less obvious symptoms, such as dizziness, sudden onset confusion, or loss of appetite. In nursing homes, altered mental status is a reliable red flag for underlying urinary tract infection.
These non-traditional symptoms make it challenging for caregivers to recognize the problem early. It’s why any significant change in an older adult’s usual behavior or mental state warrants prompt medical assessment, often including a urine culture.
Non-Specific Symptoms: Confusion, Fatigue, and Other Subtle Clues of Urinary Tract Infection
Elderly patients with UTIs often display non-specific symptoms such as sudden confusion or delirium, unexplained fatigue, loss of balance, or even falls. Unlike in younger adults, fever may be mild or completely absent. Caregivers and healthcare providers must consider UTI symptoms even in the absence of pain or urinary complaints if mental status changes arise.
Increased confusion
Incontinence
Falls
Fever
Pain or burning during urination
Changes in urine color or odor

Identifying Symptoms of UTIs vs. Other Health Conditions in Older Adults
Because symptoms like confusion or lethargy overlap with other serious medical conditions—such as dehydration, stroke, or medication reactions—diagnosing a urinary tract infection in elderly persons often requires comprehensive evaluation. Medical providers use urine cultures, medical history, and physical exams to distinguish between urinary tract infection and other causes.
When mental or physical changes appear suddenly and cannot be attributed to a known illness or medication, always consider a urinary tract infection as a possible cause and consult a healthcare provider for appropriate testing.
Testing and Diagnosis: Proper Steps for Suspected Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly
If a urinary tract infection is suspected in an older adult, it’s vital to follow appropriate testing protocols. Relying solely on symptoms may result in either missed diagnoses or unnecessary antibiotic use. Urine cultures and sensitivity testing remain the gold standard for confirming a UTI and choosing the right antibiotic, especially in cases of frequent UTI or antibiotic resistance.
Avoiding over-treatment is equally important. Not every older adult with bacteria in their urine (asymptomatic bacteriuria) requires antibiotics unless they are symptomatic or undergoing specific procedures.
When to Request a Urine Culture for Suspected Urinary Tract Infection
A urine culture should be obtained when an older adult presents with new or acute symptoms suggestive of a urinary tract infection—such as sudden confusion, fever, or urinary complaints. This diagnostic step is crucial for guiding effective treatment and ruling out other conditions.
For nursing home residents or hospitalized individuals, urine cultures may be more frequently employed due to the higher risk of atypical symptoms and resistant bacterial strains. Timely urine testing can prevent complications and promote rapid recovery.
Avoiding Unnecessary Treatment: Distinguishing UTI from Asymptomatic Bacteriuria
As growing concerns about antibiotic resistance mount, healthcare providers recommend NOT treating asymptomatic bacteriuria in most older adults. The presence of bacteria in the urine without symptoms does not require intervention—except in specific situations like an upcoming urologic procedure.
Using antibiotics only when truly needed reduces the risk of side effects and the spread of resistant bacteria, which is an especially important strategy in nursing home and hospital settings.
Effective Treatment and Relief for Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly
Immediate and appropriate treatment is essential to minimize discomfort and reduce complications from urinary tract infections in elderly patients. The mainstay of therapy is antibiotics, tailored to the specific bacteria identified via urine culture. However, clinicians balance the need for prompt symptom relief with the goal of preventing antibiotic overuse and resistance.
Proper hydration, pain management, and attentive monitoring help support recovery and prevent setbacks or recurrent UTI episodes.
First-Line Antibiotics and Alternative Options for Older Adults
Treatment of urinary tract infections in older adults usually begins with first-line antibiotics such as nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, or fosfomycin. Which antibiotic is selected depends on the type of bacteria found and local patterns of antibiotic resistance. In cases of allergy, intolerance, or recurrent UTI, second-line therapies or longer courses may be necessary.
For complicated infections or kidney involvement, IV antibiotics or hospitalization may be required. Every treatment plan should involve a careful review of allergies, potential medication interactions, and the patient's overall health condition.

Managing UTI Symptoms and Supporting Recovery in Older Adults
Aside from antibiotics, older adults with urinary tract infections benefit from supportive care: staying hydrated, using pain relievers when appropriate, and ensuring proper nutrition. Ensuring easy and frequent access to bathroom facilities and maintaining personal hygiene are also important to comfort and speed recovery.
Rest, attentive monitoring for worsening symptoms, and regular follow-up with healthcare providers further safeguard against complications and promote complete recovery.
“Rapid treatment of urinary tract infections in elderly can dramatically improve the chance of a quick, full recovery.”
Watch: Short explainer on signs, diagnosis, and relief tips for urinary tract infections in elderly.
Prevention: How to Prevent UTIs in Older Adults and Reduce Recurrence
Preventing urinary tract infections in elderly is always preferable to treating them. Strategies focus on minimizing known risk factors, improving hygiene, and making health-promoting lifestyle changes. Attention to hydration and bathroom routines plays a significant role in reducing recurrence risk.
Empowering both older adults and caregivers with education and tools can make a significant difference in the incidence of tract infections and their associated health consequences.
Best Practices for Preventing Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly
A combination of lifestyle habits and smart healthcare practices is the best way to prevent UTIs in older adults. Key steps include drinking adequate fluids (unless medically contraindicated), maintaining regular toileting, and practicing good personal hygiene. Incontinence management and catheter care should follow best practice guidelines.
Hydration
Proper hygiene
Addressing health conditions that increase risk
Using catheters only when necessary
Regular toileting routines

The Role of Probiotics and Lifestyle Changes for Urinary Tract Health
Some studies suggest that probiotics —especially those containing lactobacillus strains—may help restore the natural balance of bacteria in the gut and urinary tract. Although research is ongoing, maintaining a healthy diet rich in probiotic foods (like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut) and low in refined sugars can support overall urinary tract health in older adults.
Other lifestyle modifications, such as regular physical activity, avoiding unnecessary antibiotics, and quitting smoking, further strengthen the body's defenses against bacterial invasion. For many seniors, these manageable changes can make a real difference in long-term UTI prevention.

People Also Ask About Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly
What is the most common cause of UTI in the elderly?
The most common cause of urinary tract infections in elderly individuals is Escherichia coli (E. coli) , a type of bacteria that normally lives in the digestive tract. In older adults, these bacteria can more easily enter and colonize the urinary tract, often due to factors like decreased mobility, weakened immune system, and use of urinary catheters.
Can elderly recover from UTI?
Yes, with prompt diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic therapy, most elderly patients can recover fully from a urinary tract infection. Supportive care, monitoring, and addressing any underlying risk factors are important to ensure a quick and complete recovery. Early intervention is key to reducing complications.
How to get rid of nausea from UTI?
Nausea related to urinary tract infection in elderly can be managed by treating the infection itself (usually with antibiotics) and ensuring proper hydration. Anti-nausea medications may be prescribed for severe cases. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare provider to exclude more serious complications.
What is the mortality rate for UTI in the elderly?
While the vast majority of urinary tract infections in elderly are treatable, the mortality rate can increase if the infection spreads to the kidneys or bloodstream, especially in frail or immunocompromised individuals. The risk of serious outcomes underscores the need for early recognition and intervention.
Frequently Asked Questions About Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly
What makes older adults more susceptible to urinary tract infections?
Age-related weakening of the immune system, chronic illnesses, use of catheters, and changes in urinary and genital anatomy all increase susceptibility.Can asymptomatic bacteriuria be left untreated in the elderly?
In most cases, yes. Treatment is only recommended if symptoms develop or if the individual is undergoing a procedure that involves the urinary tract.How often should urine cultures be performed in older adults?
Urine cultures are recommended only when new symptoms suggest a UTI is present. Routine testing without symptoms is generally not recommended to avoid unnecessary antibiotics.Are there natural remedies safe for elderly with urinary tract infection?
Maintaining hydration and personal hygiene are the safest non-antibiotic approaches. Always check with a healthcare provider before trying supplements or herbal remedies, as not all are safe for older adults or those on medications.How do providers distinguish between tract infection and other health conditions in older adults?
Providers rely on clinical assessment, patient history, physical exams, and urine testing to differentiate urinary tract infections from other causes of symptoms.
Quick Reference Guide: Urinary Tract Infections in Elderly Prevention and Relief Strategies
Quick Relief Tips |
Prevention Measures |
|---|---|
Start antibiotics promptly after urine culture confirmation |
Drink adequate fluids (unless restricted) |
Manage pain with recommended medications |
Follow good hygiene practices |
Monitor for worsening or new symptoms |
Empty bladder regularly and completely |
Encourage rest and nutrition |
Use catheters only when necessary |

Empowering Older Adults: Take Control Against Urinary Tract Infections Today
Older adults and caregivers should feel empowered to take action at the first sign of a urinary tract infection. Recognizing symptoms quickly, following up with healthcare providers, maintaining good hydration and hygiene, and practicing prevention can dramatically reduce the risk of complications and improve quality of life for older adults. Share this guide with those you care for to help protect and support urinary tract health.
“Proactive prevention and immediate action are key to safeguarding the urinary tract health of older adults.”
Take charge of urinary tract health today—know the signs, act quickly, and support prevention strategies for safer, healthier aging.
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a significant health concern among older adults, often presenting with atypical symptoms such as confusion, fatigue, or dizziness, which can lead to misdiagnosis and inappropriate antibiotic use. This mismanagement not only contributes to antibiotic resistance but also overlooks other potential underlying conditions. For a comprehensive understanding of this issue, consider reading How UTIs Became One of the Most Common Misdiagnoses in American Medicine .
Additionally, recognizing the unique symptoms and implementing effective prevention strategies are crucial in managing UTIs in the elderly. The article UTIs in the Elderly: Symptoms, Treatments, and Prevention offers valuable insights into identifying symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures tailored for older adults.
If you’re serious about safeguarding the health of elderly individuals, these resources will provide you with essential knowledge and practical strategies to effectively manage and prevent urinary tract infections.
Article provided by:
Kenneth D. St. Pé, APLC
Address: 700 St John St #401, Lafayette, LA 70501
Phone: (337) 534-4043
Website: stpelaw.com
Facebook: facebook.com/stpelawfirm
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment