Did you know that thousands of older adults in nursing homes and care facilities succumb to preventable infections each year—often from causes as simple as poor hand hygiene or overlooked cleaning protocols? These are not inevitable outcomes. By mastering infection control protocols in elder care, you can dramatically reduce risk and save lives. This guide reveals the most effective, science-backed approaches, hands-on tools, and best practices to protect the vulnerable residents you care for. Dive in to learn essential protocols that set top-performing facilities apart and ensure the safety of both residents and staff.

Why Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care Are Critical: An Uncomfortable Truth
Every year, thousands of older adults in nursing homes and care facilities lose their lives to preventable infections. With infection prevention and control protocols, these numbers can drastically decrease. Discover the science-backed approaches leading facilities use to keep residents safe and reduce infectious disease outbreaks.
For those working in elder care, the importance of infection control protocols cannot be overstated. Older adults—often living with chronic conditions or weakened immune systems—are at higher risk for infectious diseases. This risk is compounded in group environments like nursing homes and term care facilities, where direct contact, shared surfaces, and communal spaces increase the chance for germs to spread. Without tight infection prevention and control, even a minor oversight can escalate into an outbreak affecting dozens. In many cases, such outbreaks could be prevented through adherence to evidence-based protocols.
Implementing robust infection control isn't just a formality; it’s a moral obligation and lifesaving necessity. By prioritizing regular hand hygiene, consistent use of personal protective equipment, effective cleaning, and education, facilities can break the cycle of transmission. As we uncover these protocols, you’ll see how a combination of training, awareness, and environmental control fosters safer care facilities and a healthier, happier resident community.
What You'll Gain: Mastering Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
Understand the essential infection control procedures in elder care environments
Apply the five pillars (5 F’s) of infection prevention and control
Implement hand hygiene and use of personal protective equipment best practices
Evaluate protocols for controlling infectious diseases
Utilize tables, lists, and real-world examples for immediate practical application
Whether you’re a nurse, manager, care provider, or family member advocating for a loved one, this guide will give you the practical tools you need to prevent the spread of infection in every elder care setting. Each section is filled with clear examples, actionable lists, and step-by-step infection control practices to strengthen your infection prevention and control knowledge. You'll gain insights not only on what protocols entail, but how to implement them successfully and adapt them to acute care challenges, especially in environments like nursing homes and term care facilities.
Explore essential concepts like environmental cleaning, staff education, emergency preparedness, and the 5 F’s of infection control. Throughout, you’ll find answers to common “People Also Ask” questions and discover how leading care facilities use advanced strategies to curb infectious disease. By mastering these best practices, you'll contribute to safer, more resilient environments for older adults.
The Foundations of Infection Control: Safeguarding Older Adults in Nursing Homes and Care Facilities

Infection control protocols in elder care are established to save lives, minimize health complications, and support continuity of care for some of our most vulnerable community members. Within nursing homes and term care facilities, even minor lapses in protocol can have major ripple effects, given the close proximity of residents and the frequent movement of staff, visitors, and service providers.
Effective infection prevention starts with a robust understanding of the unique challenges faced by older adults, such as weaker immune responses, existing health issues, and frequent need for acute care intervention. Protocols are designed to ensure every aspect of care—from admission to daily routines and emergencies—fulfills stringent, evidence-based standards. This means facilities must demonstrate ongoing compliance with regulatory guidance and standardization across care teams.
Understanding Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care and Elderly Nursing Homes
Defining infection control protocols in elder care and long-term care facilities
Compliance and standardization in nursing homes and acute care
Challenges unique to older adults and term care environments
Infection control protocols in elder care comprise structured practices and policies tailored to reduce the risk of infection for older adults living in group settings. Protocols cover a spectrum of interventions: hand hygiene, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), environmental cleaning, cohorting during outbreaks, and swift response to emerging infections. For term care facilities and nursing homes , following national and local guidelines (such as those from CDC.gov websites) is a minimum requirement. However, consistent staff training and compliance monitoring elevate these standards into daily practice.
Standardization is essential; effective infection prevention and control must be enforced uniformly.
Older adults often experience age-related physiological changes and multiple comorbidities, which increase susceptibility to infections and slow recovery times.
Challenges include resident mobility limitations, cognitive impairment, high antibiotic use, and staff turnover— each imposing unique barriers to optimal infection control practice.
" Infection prevention and control protocols are the single most effective intervention for saving lives in care facilities. "
— Infection Prevention Specialist, CDC
Key Principles of Infection Prevention and Control for Older Adults
Transmission mechanisms of infectious diseases in older adult populations
Role of health care teams and care providers in long-term care settings
Overview: infection risks and typical control failures in nursing homes
Understanding how infectious disease spreads within care facilities is the first step toward effective prevention. Pathogens can be transmitted by direct contact (touch), droplets (coughing, sneezing), air (aerosols), or indirect transfer via fomites (shared objects or surfaces). In older adult populations, communal living amplifies these risks. Memory impairment can lead to overlooked hygiene, and limited mobility can prevent frequent hand washing.
The entire health care team —from cleaning staff and aides to nurses, administrators, and visitors—plays a pivotal role in implementing infection control protocols in elder care. Typical control failures in nursing homes include insufficient hand hygiene, lack of PPE, delayed isolation of symptomatic residents, and inadequate cleaning, all of which provide opportunities for pathogens to flourish. Proactive prevention and rapid control are critical to safeguarding residents and upholding public health standards.

Table: Common Pathogens in Nursing Homes and Infection Control Responses
Pathogen |
Common Outbreak Site |
Recommended Infection Control Protocol |
|---|---|---|
Norovirus |
Nursing Homes |
Strict hand hygiene, isolation protocols, surface disinfection |
Influenza |
Care Facilities |
Vaccination, PPE usage, respiratory etiquette |
MRSA |
Term Care Facilities |
Contact precautions, diligent hand hygiene, decontamination |
Care facilities must remain vigilant, as outbreaks of norovirus, influenza, and MRSA occur frequently and cause serious complications. Applying the right infection control protocols in elder care stops these infections at the source—protecting older adults and maintaining public trust in your facility.
Standard Precautions: Core Infection Prevention Practices in Elder Care
The cornerstone of infection prevention and control in any nursing home or term care setting is the diligent application of standard precautions. These strategies—rooted in science and designed for practical use in real-world care facilities—are proven to prevent the spread of infection among residents and staff. Implementing them thoroughly means making safety a baseline, not an exception.
From routine hand hygiene to PPE usage, and environmental cleaning, these protocols must be part of every daily shift, with monthly infection prevention workshops reinforcing their importance. Personal protective equipment and strict hygiene standards are non-negotiable aspects of quality elder care.
Implementing Hand Hygiene Protocols in Nursing Homes and Term Care Facilities
When and how often should hand hygiene be practiced?
Hand sanitizer versus traditional soap-and-water in acute care
Role of staff, care provider, and visitor compliance
Hand hygiene is the single most effective method of preventing infection transmission within nursing homes and term care facilities. Staff, visitors, and residents alike must understand and commit to frequent hand cleansing—particularly before and after resident contact, bathroom visits, meal times, and after touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
Hand sanitizers (alcohol-based) offer convenience and efficacy for most routine events, especially where access to sinks is limited. However, proper soap-and-water washing remains critical when hands are visibly soiled or after caring for residents with certain infectious diseases. Ongoing education and reminders—like posters, digital signage, and daily verbal prompts—are essential to ensuring compliance and creating a culture of infection prevention.
Proper Use and Disposal of Personal Protective Equipment in Elder Care Settings
Types of personal protective equipment needed for various infectious disease scenarios
Stepwise guidance: donning and doffing PPE in nursing homes and term care facilities
Ensuring supply chain resilience for personal protective equipment
PPE—such as gloves, gowns, face masks, goggles, and face shields—serves as the first line of defense against infectious agents in acute care and long-term care settings. The correct use and disposal of these items are critical to their effectiveness. Every staff member must know the proper order for donning (putting on) and doffing (removing) PPE to avoid contamination, and facilities should regularly check PPE supply chains to prevent shortages during outbreaks.
Instructional signage and routine staff training ensure that care providers understand and follow these critical steps. Disposable PPE must be used once and discarded according to infection control policy; reusable items must undergo proper cleaning and disinfection. As part of a comprehensive infection control protocol in elder care , these standards substantially reduce the risk of pathogen transmission.

Cleaning, Disinfection, and Environmental Control in Care Facilities
Environmental cleaning schedules in long-term care environments
High-touch surface disinfection best practices
Role of environmental staff in infection prevention
The physical environment in nursing homes and term care facilities can quickly become a hub for pathogens if cleaning schedules are lax. Environmental cleaning must follow a rigorously tracked schedule—resident rooms should be cleaned daily and shared areas multiple times per day. High-touch surfaces (doorknobs, call buttons, bed rails) are the primary sites of germ transfer and must be prioritized.
Environmental staff are key players in infection prevention and control. Their work, backed by detailed logs and monthly audits, ensures compliance and enables quick identification of lapses. When everyone has a role in enforcing high cleaning standards, the risk of infection drops dramatically for all residents, staff, and visitors.
Daily cleaning log for resident rooms
Weekly deep-clean protocols for shared equipment
Monthly auditing and reporting mechanisms

Advanced Infection Control Strategies: Prevention and Control of Infectious Disease Outbreaks
To stay one step ahead of emerging threats, forward-thinking care facilities go beyond basic protocols—developing advanced infection control strategies for pandemic preparedness and outbreak management. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for robust disease control and prevention frameworks that are adaptable, proactive, and well-coordinated with acute care facilities and local public health authorities.
Such strategies include quarantine protocols, cohorting (grouping infected or at-risk residents), emergency response teams, and real-time communication with acute care providers. Close monitoring, quick action, and cross-sector coordination ensure that facilities contain outbreaks and minimize disruption to resident routines.
Infection Prevention and Pandemic Preparedness in Long-Term Care Facilities
Outbreak response teams and disease control collaboration
Quarantine procedures and cohorting techniques
Cross-sector coordination with acute care providers
During an emerging outbreak, specially trained response teams activate detailed protocols at every level—from isolating symptomatic residents to ramping up environmental cleaning and deploying reserves of PPE. Quarantine and cohorting is used to prevent cross-infection, designating specific areas or staff for affected residents. Successful facilities maintain regular shared drills and simulation exercises to keep all staff confident and prepared.
Partnerships with acute care and other health care providers facilitate rapid evacuations, supply sharing, and information exchange. This ensures no facility is left isolated during crises—a lesson reinforced throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.

Special Focus: Preventing Urinary Tract and Respiratory Tract Infections
Best practices for urinary tract infection control
Managing respiratory tract infection exposure: mask protocols, ventilation, patient isolation
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) and respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are among the most common and dangerous illnesses afflicting older adults in care settings. Best practices for UTI control include routine toileting, proper perineal hygiene, avoiding unnecessary catheterization, and prompt recognition of infection signs. Staff should receive regular training on correct catheter care and documentation within electronic health records.
Managing respiratory tract infection exposure involves enforcing mask protocols, maintaining proper ventilation throughout the facility, and isolating symptomatic residents. Staff must be educated to recognize early symptoms—such as fever, cough, or confusion—and implement isolation protocols immediately. These measures drastically reduce secondary infection rates and improve outcomes for vulnerable older adults.
Training, Audits, and Continuous Improvement for Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
Regular staff training and drill exercises
Audit checklists for infection control compliance
Continuous feedback mechanisms for process improvement
Ongoing training and auditing ensure infection control protocols in elder care achieve real impact, not just compliance on paper. Monthly infection prevention workshops, simulation drills, and regular review of infection rate data foster a knowledgeable, alert team. Using detailed audit checklists, supervisors can monitor where protocols break down—from missed hand hygiene moments to skipped PPE changes—and provide real-time coaching or retraining.
Continuous improvement involves listening to frontline staff, inviting feedback, and adapting protocols to new challenges. By establishing a cycle of learning, assessment, and rapid adjustment, high-performing facilities minimize infection risks and maintain trust among residents, families, and regulators.

Best Practice Lists for Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
Daily shift reminders for hand hygiene and PPE
Monthly infection prevention workshops
Emergency response plans for infectious disease outbreaks
Every successful infection control program features well-documented routines, from daily shift reminders and signage to reinforce correct hand hygiene and PPE use, to monthly training sessions updating staff on new threats or guidelines. Clear emergency response plans pre-positioned throughout the facility enable a rapid, organized outbreak response—ensuring every team member knows their role.
These simple, consistent measures form the backbone of infection control protocols in elder care , proving that a proactive rather than reactive stance is essential to keeping older adults safe.
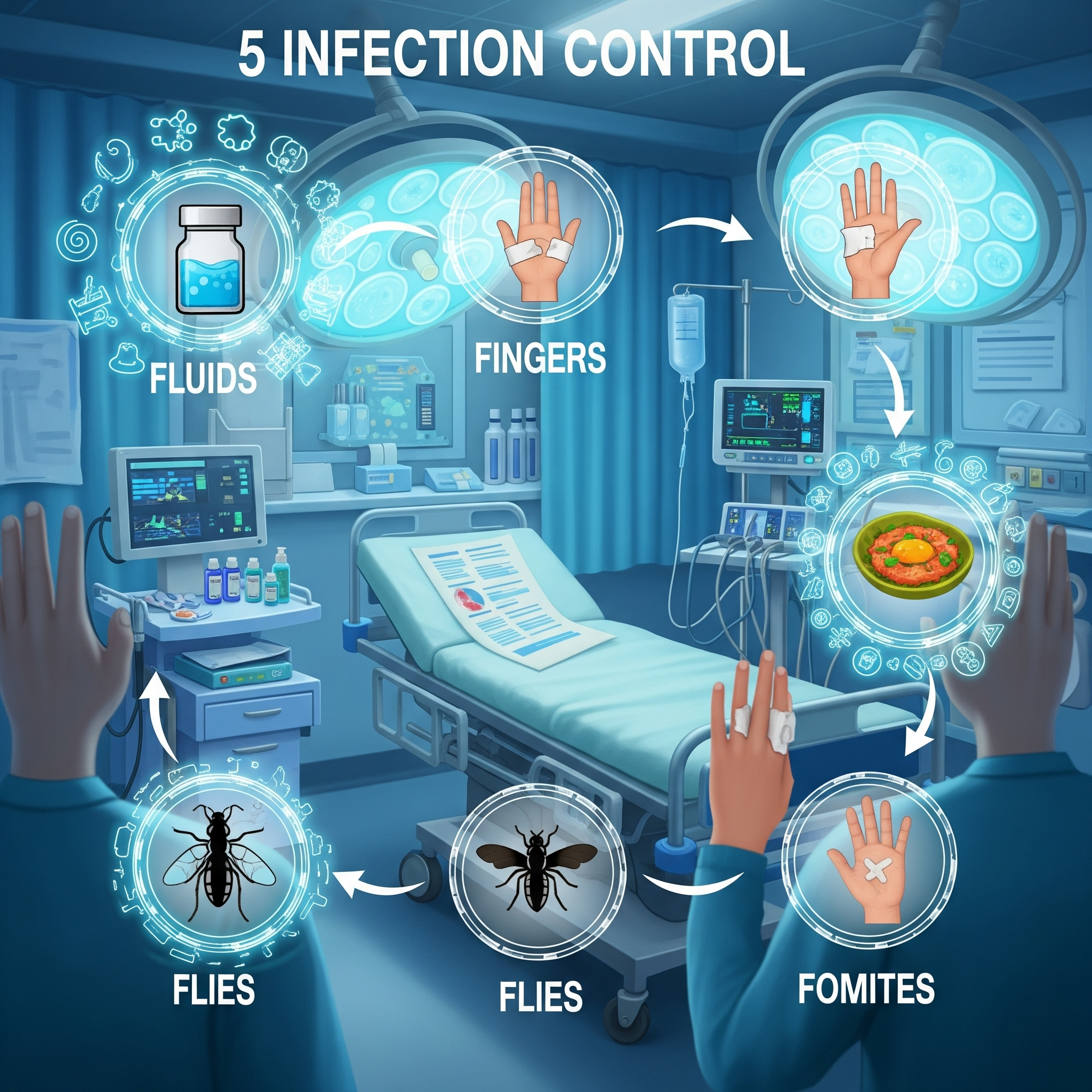
People Also Ask: What are the 5 F's of infection control?
Understanding the Five F's and Their Role in Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
Fluids, Fingers, Food, Flies, and Fomites
Application in nursing home and term care facility protocols
The “ 5 F’s of infection control ”—Fluids, Fingers, Food, Flies, and Fomites—are memorable reminders of the key ways infections spread in elder and term care environments. Fluids (such as saliva, urine, blood) are common carriers of pathogens; strict handling and disposal reduce risk. Fingers remain a primary mode for transmitting germs, especially when staff or residents forget to wash hands after contact with surfaces or bodily fluids.
Food can harbor bacteria if preparation or serving standards slip. Flies (and other insects) serve as mechanical carriers in indoor environments, especially in warmer climates or older buildings. Finally, fomites (shared objects like remote controls, dining utensils, or wheelchairs) facilitate cross-contamination when not regularly disinfected. Recognizing and controlling these five elements is fundamental in every modern infection control protocol.
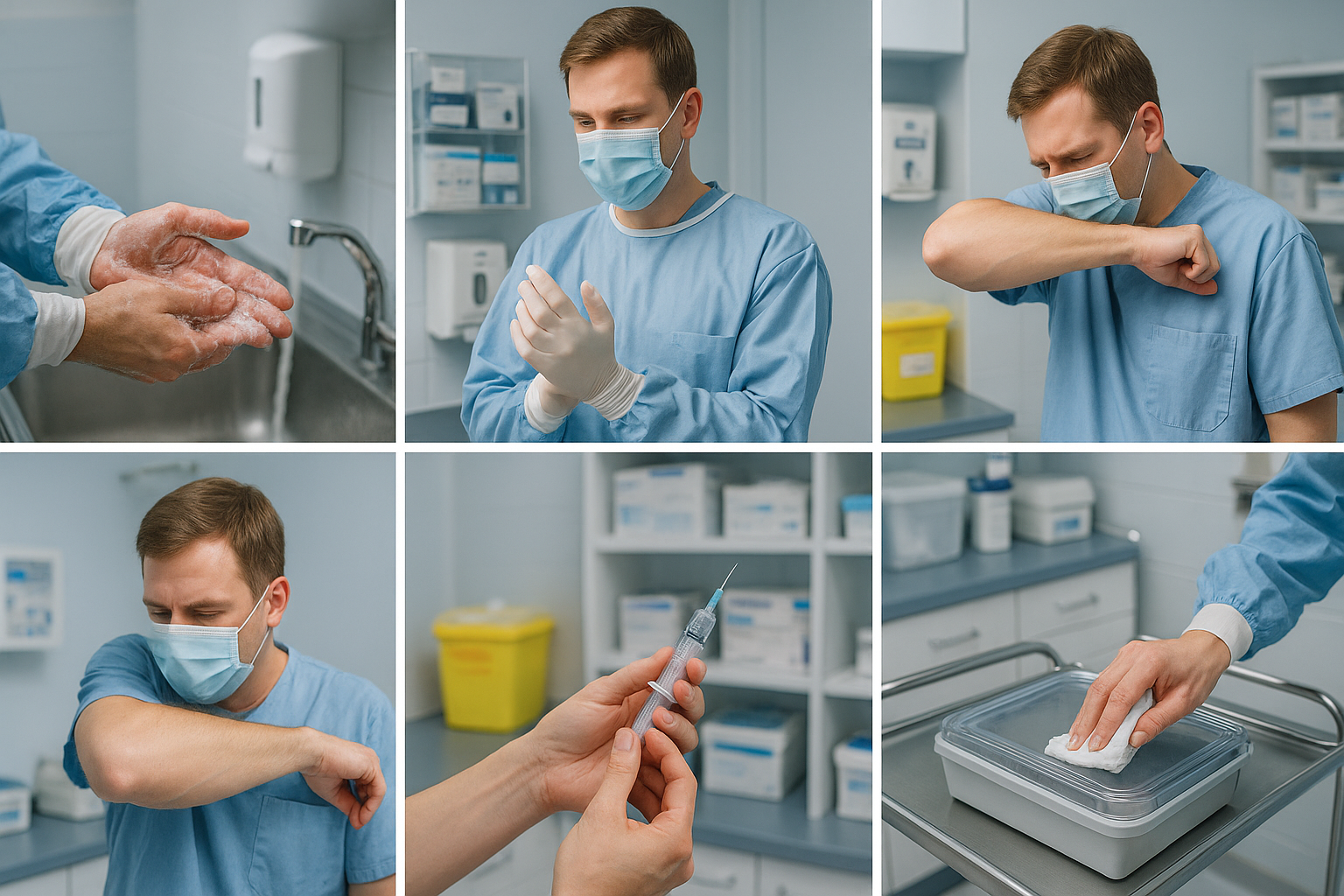
People Also Ask: What are the 5 basic principles for infection control?
Exploring the Five Basic Principles Driving Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
Hand hygiene, PPE, respiratory hygiene, safe injection practices, safe handling of potentially contaminated equipment/surfaces
Real-life examples in long-term and acute care
The five basic principles of infection control are universally applicable to all healthcare settings, including elder and term care facilities:
Consistent hand hygiene before/after resident contact or surface contact
Proper and regular use of personal protective equipment
Respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette (covering coughs, masks when needed)
Following safe injection practices (single-use needles, sterile technique)
Careful handling and disinfection of all potentially contaminated equipment and surfaces
People Also Ask: What are infection control procedures in aged care?
Step-by-Step Infection Control Procedures in Elder Care and Term Care Facilities
Routine practices for standard and transmission-based precautions
Integration within electronic health record systems to monitor compliance
Infection control procedures in aged care start with routine practices applicable to every resident, regardless of known disease status. This includes standard precautions (hand hygiene, PPE, environmental cleaning) and transmission-based precautions (isolation, enhanced PPE) for confirmed or suspected infections.
Modern facilities integrate these practices with electronic health record (EHR) systems, promoting consistent documentation and easy monitoring of protocols. Supervisors can track hand hygiene compliance, cleaning schedules, isolation orders, and PPE use—providing real-time coaching as necessary. Regular review of this data improves accountability and program effectiveness.

People Also Ask: What are the 5 standard precautions for infection control?
Breaking Down the Five Standard Precautions Used in Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
Personal protective equipment, hand hygiene, respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette, safe injection practices, safe handling of contaminated items
Practical applications for older adults in nursing homes
The five standard precautions are the pillars upon which infection control protocols in elder care rest:
Wearing personal protective equipment when interacting with bodily fluids or infectious materials
Strict hand hygiene at all key moments
Ensuring respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette with masks and tissues
Adhering to safe injection practices to prevent cross-contamination
Safely handling and cleaning contaminated items and equipment, keeping resident areas sanitized
Frequently Asked Questions on Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
How often should protocols be updated in elder care settings?
Infection control protocols should be reviewed and updated at least annually, or whenever state/local guidance changes, new infectious threats emerge, or after internal audits reveal opportunities for improvement. Ongoing education ensures staff remain current on best practices.Which new technologies are enhancing infection prevention practices?
Emerging tools include automated hand hygiene monitoring systems, real-time environmental cleanliness sensors, UV-C disinfection robots, and artificial intelligence-driven analytics within EHRs. Each enhances your ability to track, measure, and update protocols in step with changing risks.How can family members participate in infection control for older adults?
Family members can ask about current infection prevention measures, follow all visitor protocols (hand hygiene, PPE), encourage vaccination, and support loved ones in reporting symptoms or unsafe practices. Their partnership with facility staff is a vital line of defense.
Essential Takeaways for Implementing Life-Saving Infection Control Protocols in Elder Care
Commit staff to routine infection prevention education
Invest in up-to-date cleaning, screening, and PPE resources
Auditing and reporting for process improvements
Empowering Safer Elder Care: Apply Robust Infection Control Protocols Today
Take proactive steps in your elder care facility to implement comprehensive infection control measures
Request our downloadable guidelines and access expert-led training resources for your team
Action: Bring these protocols into daily practice—make your facility a model of safety, compassion, and infection control excellence.
To enhance your understanding of infection control protocols in elder care, consider exploring the following authoritative resources:
“Infection Prevention and Control in Long-Term Care Homes” : This comprehensive guide by Southwestern Public Health offers detailed strategies for antimicrobial stewardship, environmental cleaning, and staff education tailored specifically for long-term care settings. (swpublichealth.ca)
“Best Practices for Infection Control and Prevention in Skilled Nursing Facilities” : Provided by Qsource, this resource outlines evidence-based practices, including staff training, infection surveillance, and outbreak management, to maintain a safe environment in skilled nursing facilities. (qsource.org)
Delving into these materials will equip you with practical tools and insights to implement effective infection control measures, ensuring the safety and well-being of residents and staff in elder care facilities.
Article provided by:
Kenneth D. St. Pé, APLC
Address: 700 St John St #401, Lafayette, LA 70501
Phone: (337) 534-4043
Website: stpelaw.com
Facebook: facebook.com/stpelawfirm
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment